Describe the Bonding in Titanium Metal
Titanium metal resists corrosion as it has an impervious coating of titaniumIV oxide. There are several theories to explain this type of bonding among them the electron sea model is most popular.

Bonding In Metals The Electron Sea Model Introduction To Chemistry
Describe the bonding in titanium metal.

. Titanium is as strong as steel but is about 40 less dense and is therefore suitable for use in the aircraft industry. Metals even pure ones can form other types of chemical bonds between their atoms. Metallic bonding is a special type of bonding that holds the metals together in metal crystal.
Explain why an aluminium-titanium alloy is harder than pure aluminium. Bonding of glass and titanium for medical and other applications is challenging and has been studied extensively. Also titanium has a higher electronegativity than calcium which means it attracts valence electrons more tightly.
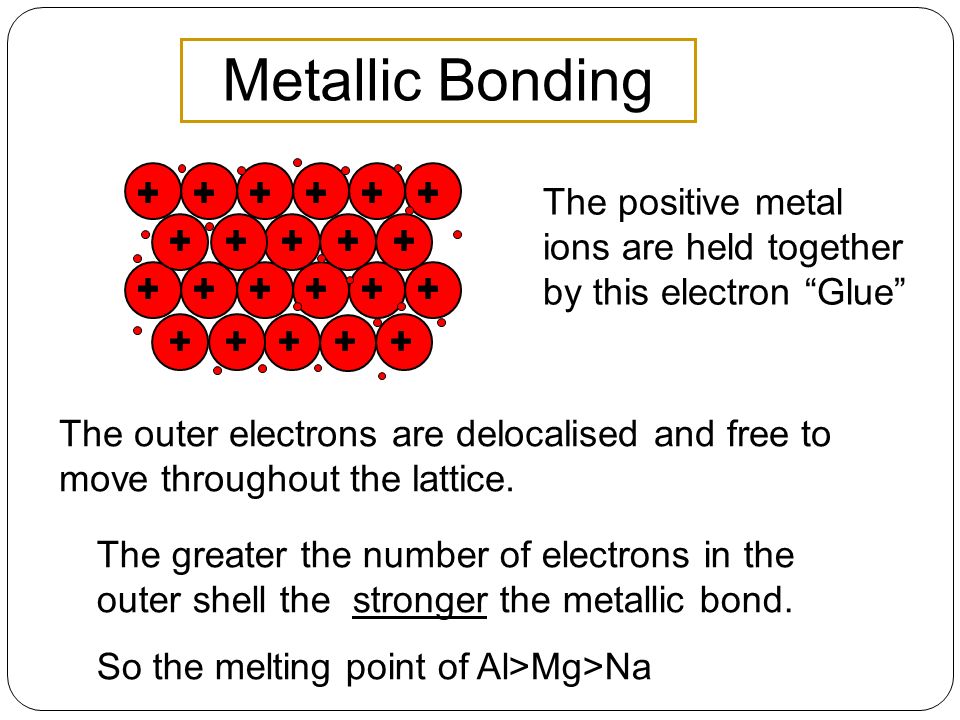
Describe the bonding in a metal and explain why metals conduct electricity 4 marks lattice of positive ions. Metallic bonding is often described as an array of positive ions in a sea of electrons. Titanium is a lightweight high-strength low-corrosion structural metal and is used in alloy form for parts in high-speed aircraft.
Stage 1 titanium ore is converted into titanium dioxide TiO 2 stage 2 titanium dioxide is then converted into titanium chloride TiCl 4. Consist of giant structures of atoms. Titanium is a low density high strength tough corrosion resistant silver colored metal.
For example graphene an allotrope of carbon exhibits two-dimensional metallic bonding. The mass spectrum of a sample of titanium gave the following data. Found in nature only as an oxide it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color low density and high strength resistant to corrosion in sea water aqua regia and chlorine.
A compound of titanium and oxygen was discovered 1791 by the English chemist and mineralogist William Gregor and independently rediscovered 1795 and. Metals form giant structures in which electrons. 3 Titanium is a metal that can be extracted from its ore in a three-stage process.
In the outer shells of the metal atoms are free to move. Titanium was discovered in Cornwall Great Britain by William Gregor in 1791 and was named by Martin. Titanium can be hammered into objects with different shapes that have similar strengthsSuggest why titanium can be hammered into different shapes.
Describe how the electrical and thermal conductivity of metals can be explained according to band theory. Nanoparticles they are smaller. Metallic bond is a term used to describe the collective sharing of a sea of valence electrons between several positively charged metal ions.
The metallic bond is the force of attraction between these free electrons and metal ions. Arranged in a regular pattern. Describe the bond in ionic bonding.
Titanium exists as several isotopes. Because titanium has more valence electrons to contribute to metallic bonding its atoms are held in place more firmly making it harder and stronger than calcium. A bond between 2 non-metals whereby one atom provides both the eletrons.
Adhesive Formulations for Bonding Titanium. Metallic bonding is the main type of chemical bond that forms between metal atoms. The electron sea model.
It is twice as strong as aluminum and 45 lighter than steel. Electrostatic attraction between a lattice of cationspositive metal ions AND a sea of delocalized electrons mobile electrons responsible for conductivity OR. Describe the bonding in metals.
Titanium is a transition metal. Metals have tendency to give up electrons and none is their to accept it. Bonding in Transition Metal Compounds and Coordination Complexes is shared under a not declared license and was authored remixed andor curated by LibreTexts.
State the number of protons neutrons and electrons in. Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Chemistry of the Transition Metals.
Up to 10 cash back Most industrial applications such as light bulbs or enameled cookware are produced by this common type of manufacturing process using high temperatures to melt the glass allowing it to wet the metal surface. Metallic bonds are seen in pure metals and alloys and some metalloids. Titanium atomsions distort the regular arrangement of atomsions OR titanium atomsions are a different size to aluminium.
Titanium Ti chemical element a silvery gray metal of Group 4 IVb of the periodic table. Calculate the relative atomic mass of titanium to two decimal places. It possesses good heat transfer characteristics and does not become magnetized.
Titanium has a high melting temperature and a density of 450 g cm3. Describe the bonding in metals. The metal is held together by the strong forces of attraction between the delocalised electrons and the positive ions.
Explain why nanoparticles pass through the skin and travel around the body more easily than normal-sized particles of titanium oxide. Beware if you are going to use the term an array of positive ions in a sea of electrons. From the outer shells of the metal atoms are.
Structure and bonding in metals Metallic bonding. Describe at the simplest level the origin of electron bands in metals. Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding and is responsible for several characteristic properties of metals such as their shiny lustre their malleability and their conductivities for heat and.
This bond is neither covalent nor ionic. Sketch out a diagram illustrating how a simple molecular-orbital approach to bonding in metals of Groups 1 and 2 always leaves some upper MOs empty. Describe metallic bonding and how it contributes to electrical conductivity.
Up to 24 cash back Titanium has four valence electrons while calcium has only two.

What Are The Bond Types In Transition Metals Quora

No comments for "Describe the Bonding in Titanium Metal"
Post a Comment